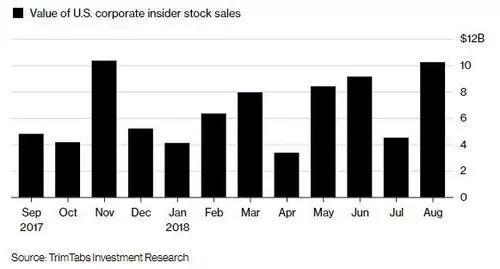
In the world of investing, dividends play a crucial role in generating income for investors. The average US stock dividend yield is a key metric that investors use to evaluate the potential returns from dividend-paying stocks. This article delves into what the average US stock dividend yield is, how it is calculated, and its significance in the investment landscape.
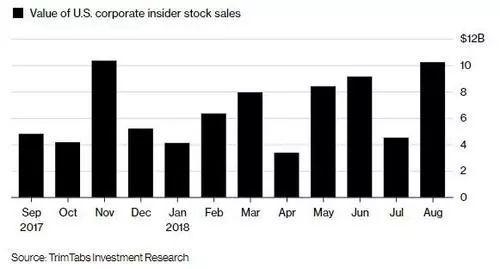
What is the Average US Stock Dividend Yield?
The average US stock dividend yield is a measure of the dividend income generated by a stock relative to its current market price. It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated by dividing the annual dividend per share by the stock's current market price. For example, if a stock pays an annual dividend of
How is the Average US Stock Dividend Yield Calculated?
To calculate the average US stock dividend yield, you need to follow these steps:
- Determine the Annual Dividend Per Share: This is the total amount of dividend paid by the company per share in a year. It can be found in the company's financial statements or by checking the stock's dividend history.
- Find the Current Market Price: This is the current price at which the stock is trading in the market. You can find this information on financial websites or stock exchanges.
- Divide the Annual Dividend Per Share by the Current Market Price: This will give you the dividend yield as a percentage.
Significance of the Average US Stock Dividend Yield
The average US stock dividend yield is a vital metric for investors for several reasons:
- Income Generation: Dividends provide a steady stream of income for investors, especially those relying on investment income for their livelihood.
- Performance Indicator: A higher dividend yield can indicate that a stock is undervalued or that the company is generating significant profits.
- Risk Assessment: Dividend yields can help investors assess the risk associated with a stock. A higher yield may suggest higher risk, as the company may be paying out a larger portion of its earnings as dividends.
Case Study: Apple Inc.
To illustrate the concept, let's consider Apple Inc. (AAPL). As of the time of writing, Apple has a dividend yield of approximately 1.2%. This means that for every
Conclusion
The average US stock dividend yield is a crucial metric for investors looking to generate income from their investments. By understanding how it is calculated and its significance, investors can make informed decisions about their dividend investments. Remember, a higher dividend yield doesn't always mean a better investment, as it's important to consider other factors such as the company's financial health and growth prospects.