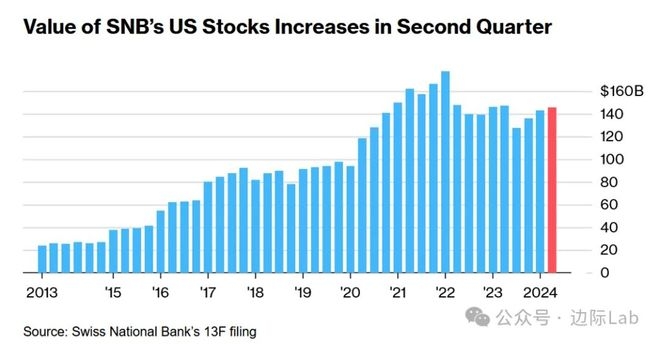
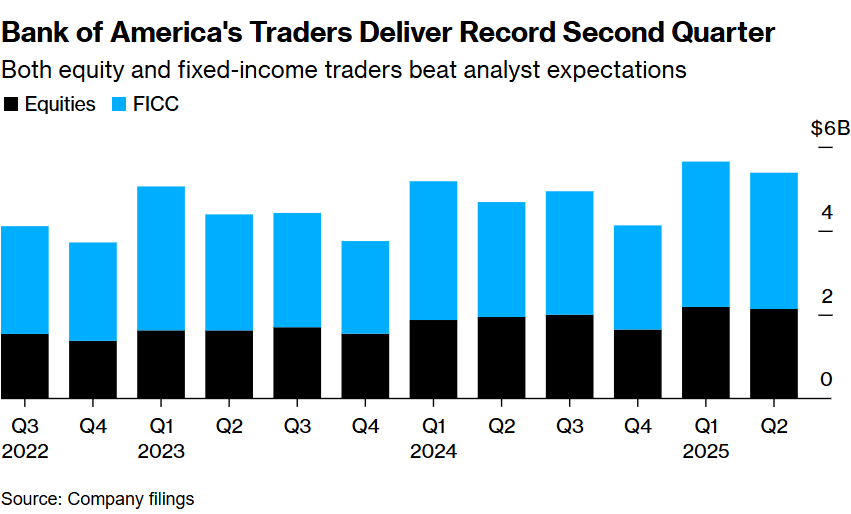
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) has long been a beacon for investors and traders worldwide. As the oldest and largest stock exchange in the United States, it offers a wide array of investment opportunities. One such opportunity is trading in NYSE futures. In this article, we delve into the world of NYSE futures, explaining what they are, how they work, and why they are crucial for investors.
What Are NYSE Futures?
NYSE futures are financial contracts that represent an agreement to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price on a specified future date. These contracts are standardized and traded on various futures exchanges, including the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the NYSE.
Key Features of NYSE Futures
- Standardization: NYSE futures are standardized in terms of contract size, quality, and delivery date. This standardization ensures liquidity and facilitates easy trading.
- Leverage: Futures trading allows investors to control a large amount of assets with a relatively small amount of capital. This leverage can amplify gains but also increase risk.
- Hedging: NYSE futures can be used to hedge against potential losses in the underlying asset. This is particularly useful for investors who own stocks or other securities in the NYSE.
How Do NYSE Futures Work?
NYSE futures work similarly to other types of futures contracts. Here's a simplified breakdown:
- Contract Specifications: Each NYSE futures contract specifies the underlying asset, contract size, delivery month, and settlement price.
- Buying and Selling: Investors can buy or sell NYSE futures contracts, depending on their investment strategy. For example, buying a futures contract at a lower price and selling it at a higher price can result in a profit.
- Expiration: NYSE futures contracts have an expiration date. At expiration, the contract is settled based on the underlying asset's price.

Why Trade NYSE Futures?
NYSE futures offer several benefits to investors:
- Leverage: As mentioned earlier, futures trading allows investors to control a large amount of assets with a relatively small amount of capital.
- Hedging: NYSE futures can be used to protect investments against market volatility.
- Diversification: Trading NYSE futures allows investors to diversify their portfolios beyond traditional stocks and bonds.
Case Study: Hedging with NYSE Futures
Imagine an investor owns a significant amount of stocks listed on the NYSE. To protect against potential losses due to market volatility, the investor decides to hedge their position using NYSE futures.
The investor buys a futures contract at a lower price, locking in a profit if the market price of the underlying asset falls. If the market price does indeed fall, the investor can sell the futures contract at a higher price, offsetting their losses in the stock market.
Conclusion
NYSE futures are a valuable tool for investors looking to diversify their portfolios, hedge against market volatility, and gain leverage. Understanding the basics of NYSE futures can help investors make informed decisions and potentially increase their returns.