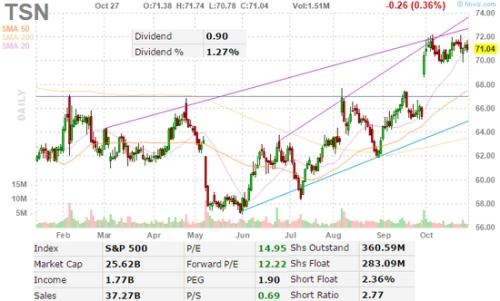
The stock market has been a cornerstone of the American economy since the early 20th century. However, it's not immune to significant downturns. Over the years, there have been several stock market crashes that have had a profound impact on the economy and investors. This article delves into the biggest stock market crashes in the United States since 1929, highlighting the causes, effects, and lessons learned from each event.
The 1929 Stock Market Crash (The Great Depression)
The 1929 stock market crash is perhaps the most famous and devastating in American history. It occurred on October 29, 1929, and is often referred to as "Black Tuesday." The crash was primarily caused by excessive speculation, overvaluation of stocks, and a lack of regulation. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) fell by 12.8% on October 29th and by 89% from its peak in September 1929 to its trough in July 1932.
The aftermath of the crash led to the Great Depression, a period of severe economic downturn that lasted from 1929 to 1939. The crash had a profound impact on the American economy, leading to widespread unemployment, bank failures, and a general decline in living standards.
The Dot-Com Bubble Burst (2000-2002)
The dot-com bubble was a period of rapid growth and speculative investment in internet-based companies during the late 1990s. However, this bubble burst in 2000, leading to a significant stock market crash. The NASDAQ Composite Index, which was heavily weighted towards technology stocks, fell by 78% from its peak in March 2000 to its trough in October 2002.
The burst of the dot-com bubble was primarily caused by excessive speculation, overvaluation of stocks, and a lack of fundamental analysis. Many investors and companies were focused on the potential of the internet and ignored the fundamentals of the businesses they were investing in.
The Financial Crisis of 2007-2008
The financial crisis of 2007-2008 was one of the most severe economic downturns since the Great Depression. It was triggered by the collapse of the housing market, excessive risk-taking by financial institutions, and the subsequent credit crunch. The DJIA fell by 54.4% from its peak in October 2007 to its trough in March 2009.
The crisis had a profound impact on the global economy, leading to widespread bank failures, government bailouts, and a significant increase in unemployment. It also highlighted the need for better regulation and oversight of the financial industry.
The COVID-19 Pandemic (2020)
The COVID-19 pandemic caused a significant stock market crash in 2020. The S&P 500 fell by 33.8% from its peak in February 2020 to its trough in March 2020. The crash was primarily caused by concerns about the economic impact of the pandemic, as well as a significant increase in volatility.
The pandemic also highlighted the importance of technology and innovation in the stock market. Many technology companies, such as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google, saw significant growth during the pandemic, as consumers turned to online shopping and remote work.
Conclusion
The stock market has been subject to several significant crashes since 1929. Each crash has had a profound impact on the American economy and investors. While these crashes have been devastating, they have also provided valuable lessons about the importance of regulation, risk management, and diversification. As the stock market continues to evolve, it's important to learn from the past and be prepared for future challenges.