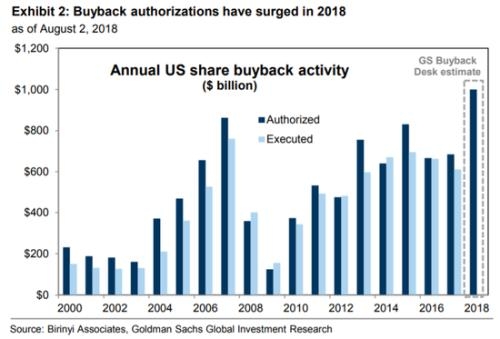
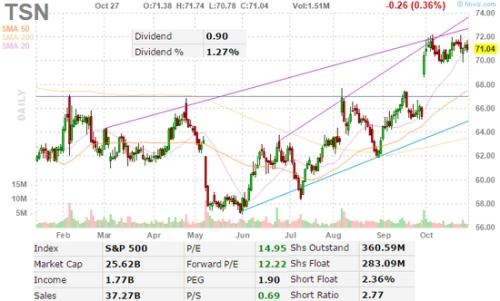
In the ever-evolving world of investments, Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) have become a popular choice for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and gain exposure to the US stock market. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding ETFs in the context of the US stock market, highlighting their benefits, risks, and key considerations for investors.
What is an ETF?
An ETF is a type of investment fund that tracks the performance of a specific index, such as the S&P 500, or a basket of assets, such as a sector or commodity. Unlike mutual funds, which are actively managed, ETFs are passively managed, meaning they aim to replicate the performance of their underlying index.
Benefits of Investing in ETFs in the US Stock Market
- Diversification: ETFs provide investors with exposure to a wide range of assets, reducing the risk associated with investing in a single stock or sector.
- Low Costs: ETFs typically have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds, making them more cost-effective for investors.
- Liquidity: ETFs are traded on exchanges like stocks, allowing investors to buy and sell shares throughout the trading day.
- Transparency: The holdings of an ETF are disclosed daily, providing investors with full transparency into the underlying assets.
Popular ETFs in the US Stock Market
- Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO): This ETF tracks the performance of the S&P 500, the most widely followed index of large-cap US stocks.
- SPDR S&P 500 ETF (SPY): Another popular S&P 500 ETF, SPY is known for its low fees and high liquidity.
- iShares Russell 2000 ETF (IWM): This ETF tracks the performance of the Russell 2000 index, which represents small-cap US stocks.
- Vanguard Information Technology ETF (VGT): This ETF focuses on the technology sector, providing investors with exposure to companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon.
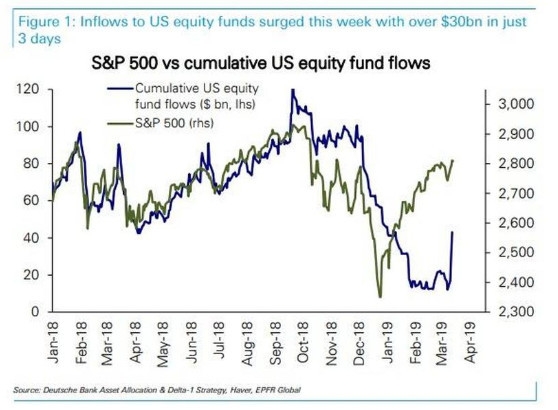
Risks of Investing in ETFs in the US Stock Market
- Market Risk: As with any investment, there is a risk that the value of an ETF could decline due to market volatility.
- Liquidity Risk: While ETFs are generally liquid, there is a risk that an ETF may become less liquid during times of market stress.
- Tracking Error: ETFs may not perfectly track the performance of their underlying index, leading to tracking errors.
Key Considerations for Investors
- Investment Goals: Investors should consider their investment goals and risk tolerance when selecting an ETF.
- Expense Ratios: Lower expense ratios can help reduce the overall cost of investing in ETFs.
- Diversification: Investors should aim to diversify their portfolios by investing in ETFs that track different asset classes and sectors.
- Tax Implications: Investors should be aware of the tax implications of investing in ETFs, particularly those that hold high-yielding assets.
Case Study: Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
One of the most popular ETFs in the US stock market is the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO). Since its inception in 2001, VOO has provided investors with exposure to the largest and most well-known US companies. Over the past decade, VOO has delivered strong returns, making it a popular choice for investors looking to invest in the US stock market.
In conclusion, ETFs offer a unique and efficient way for investors to gain exposure to the US stock market. By understanding the benefits, risks, and key considerations of investing in ETFs, investors can make informed decisions and build diversified portfolios.