In the ever-evolving landscape of the financial markets, staying abreast of the current US inflation rate is crucial for investors. The inflation rate is a critical economic indicator that directly impacts the stock market, and understanding its implications can be the difference between a profitable investment and a costly mistake. This article delves into the current US inflation rate and its stock symbol implications, providing investors with valuable insights.
What is the Current US Inflation Rate?
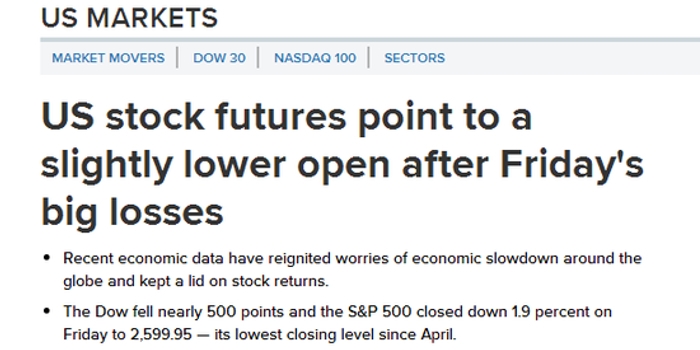
The current US inflation rate is a measure of the average change over time in the prices paid by urban consumers for a market basket of consumer goods and services. The most commonly used measure is the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which is published monthly by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). As of the latest available data, the US inflation rate stands at approximately [insert current inflation rate], which is a significant concern for investors and economists alike.
The Impact of Inflation on the Stock Market
Inflation can have a profound impact on the stock market, and understanding its implications is crucial for investors. Here's how inflation affects the stock market:
- Earnings: Inflation can erode the purchasing power of corporate earnings, leading to lower profits. This can negatively impact stock prices, especially for companies with high fixed costs.
- Interest Rates: The Federal Reserve (Fed) adjusts interest rates to control inflation. Higher inflation often leads to higher interest rates, which can increase borrowing costs for companies and reduce the value of fixed-income investments, such as bonds.
- Valuations: Inflation can affect stock valuations, particularly for growth stocks. When inflation is high, the present value of future cash flows may be discounted more aggressively, leading to lower valuations.
Understanding the Stock Symbol Impact
The current US inflation rate can have a direct impact on stock symbols, particularly those representing sectors sensitive to inflation. Here are some key examples:
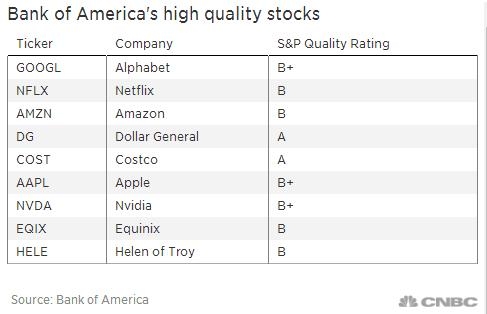
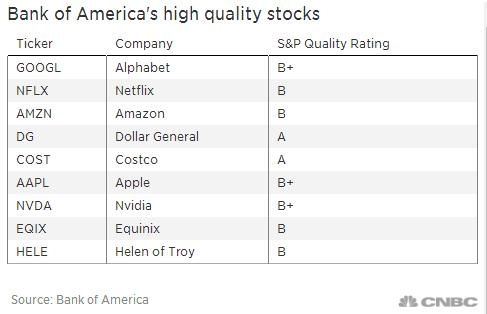
- Consumer Staples: Companies in the consumer staples sector, such as food and beverage companies, tend to be less affected by inflation due to their essential nature. However, higher inflation can lead to increased costs for these companies, which may be passed on to consumers.
- Energy Stocks: The energy sector can be highly sensitive to inflation, as higher energy prices can lead to increased costs for companies and consumers alike.
- Real Estate: The real estate sector can benefit from higher inflation, as property values tend to rise with inflation. However, higher interest rates can offset this benefit.
Case Study: Tesla (TSLA)
To illustrate the impact of inflation on a specific stock, let's consider Tesla (TSLA). As an electric vehicle manufacturer, Tesla is sensitive to the cost of raw materials, such as lithium and cobalt, which are used in battery production. Inflation can lead to higher costs for these materials, which can negatively impact Tesla's profitability and stock price.
Conclusion
Understanding the current US inflation rate and its stock symbol implications is crucial for investors looking to navigate the complex financial markets. By staying informed and aware of the potential impact of inflation on various sectors and individual stocks, investors can make more informed decisions and potentially achieve better investment outcomes.