Introduction: Investing in the stock market can be a daunting task, especially for beginners. One of the most common types of stocks that investors come across is the US common stock. In this article, we will delve into the basics of US common stock, its features, and the benefits it offers to investors. By the end of this article, you will have a clearer understanding of what US common stock is and how it can be a valuable addition to your investment portfolio.
What is US Common Stock?
US common stock represents ownership in a company. When you purchase a common stock, you become a partial owner of the company, with the number of shares you own determining your ownership stake. As a shareholder, you have the right to vote on certain corporate decisions and receive dividends, if any, paid out by the company.
Key Features of US Common Stock:
Ownership Stake: As mentioned earlier, US common stock gives you a piece of ownership in the company. This means that you can benefit from the company's growth and success.
Voting Rights: Common stockholders have the right to vote on certain corporate decisions, such as electing the board of directors and approving major corporate actions.
Dividends: While not guaranteed, common stockholders may receive dividends, which are a portion of the company's profits distributed to shareholders.
Capital Gains: If the value of the stock increases, you can sell it at a higher price and make a profit, known as capital gains.
Risk: Common stocks are generally riskier than other types of investments, such as bonds, as shareholders are last to receive any assets in the event of bankruptcy.
Understanding Dividends:
Dividends are payments made by a company to its shareholders from its profits. They can be in the form of cash or additional shares of stock. While dividends are not guaranteed, some companies have a long history of paying dividends to their shareholders.
Types of Dividends:
Cash Dividends: The most common form of dividends, where shareholders receive cash payments.
Stock Dividends: Additional shares of the company's stock are distributed to shareholders instead of cash.
Property Dividends: Dividends paid in the form of assets, such as real estate or other securities.
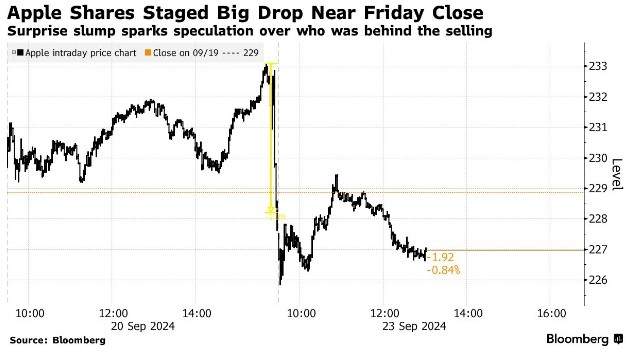
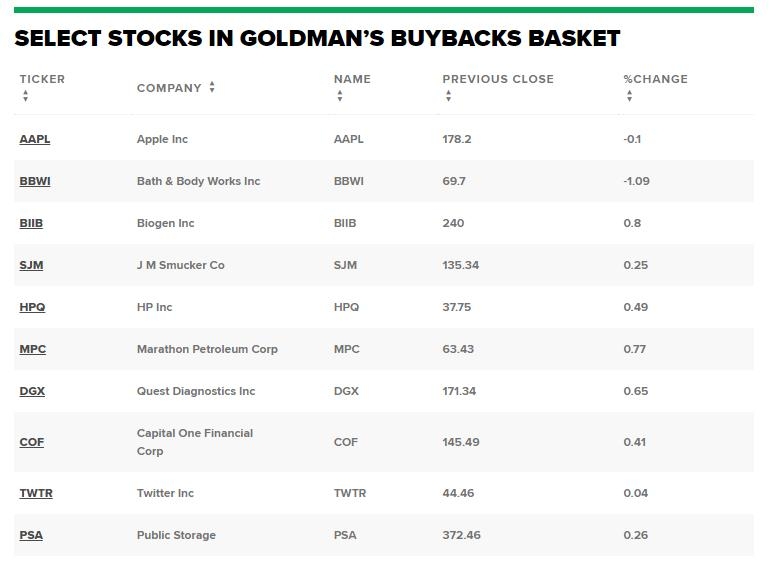
Case Study: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Apple Inc. is a prime example of a company that offers US common stock. As a leading technology company, Apple has seen significant growth over the years, making it an attractive investment for many investors. By purchasing Apple common stock, investors can benefit from the company's growth and receive dividends, if any, paid out by the company.
Conclusion:
US common stock is a vital component of any investment portfolio, offering potential for growth, dividends, and voting rights. While it comes with its own set of risks, understanding the basics of US common stock can help investors make informed decisions. As always, it is essential to do thorough research and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.