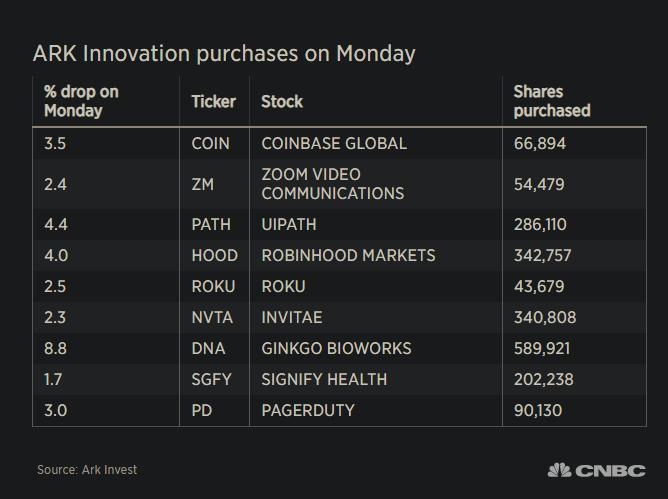
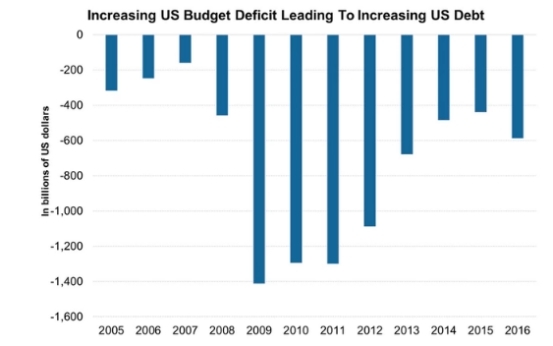
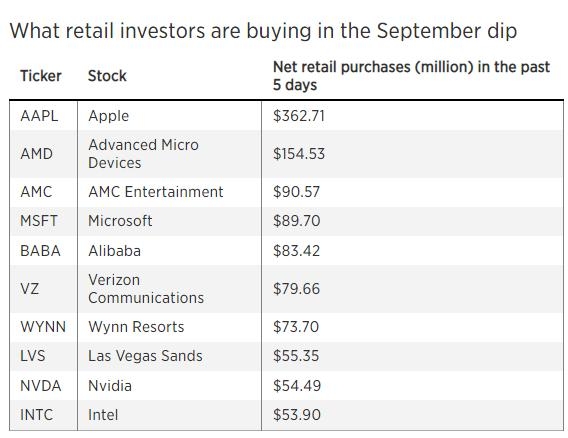
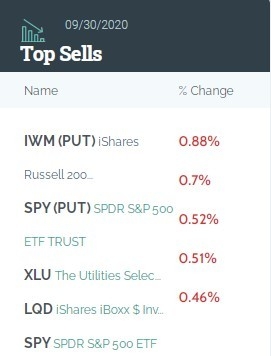
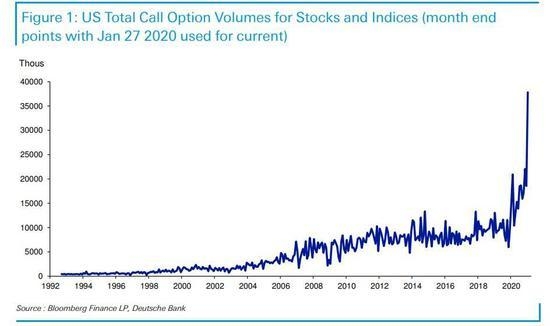
The stock market is a cornerstone of the American economy, and its rich history spans centuries. If you're curious about how long the US stock market has been around, you're in for a fascinating journey through time. In this article, we'll delve into the origins of the stock market in the United States and explore its evolution over the years.
The Beginnings of the Stock Market
The US stock market has its roots in the colonial era. The Boston Stock Exchange (now known as the Boston Stock Exchange Group), which is the oldest stock exchange in the United States, was established in 1792. However, the first organized stock exchange was the New York Stock and Exchange Board (now the New York Stock Exchange, or NYSE), which was founded in 1792 as well.
The Buttonwood Agreement, signed by 24 men under a buttonwood tree in New York City, laid the foundation for the stock market. This agreement, dated May 17, 1792, established the rules and regulations for the exchange. It was a significant milestone in the history of the US stock market, as it marked the beginning of a formalized system for buying and selling stocks.
The Evolution of the Stock Market
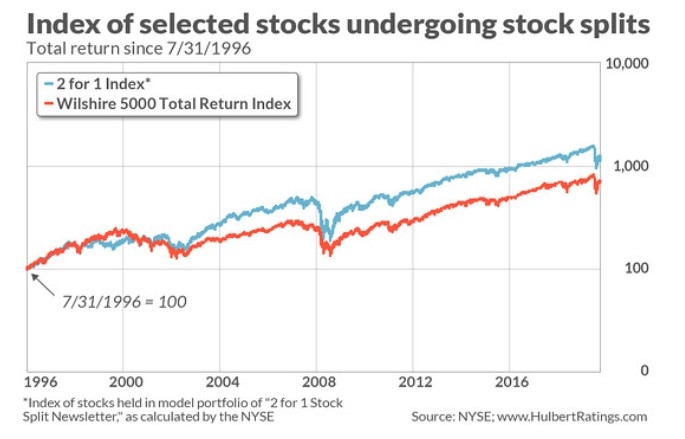
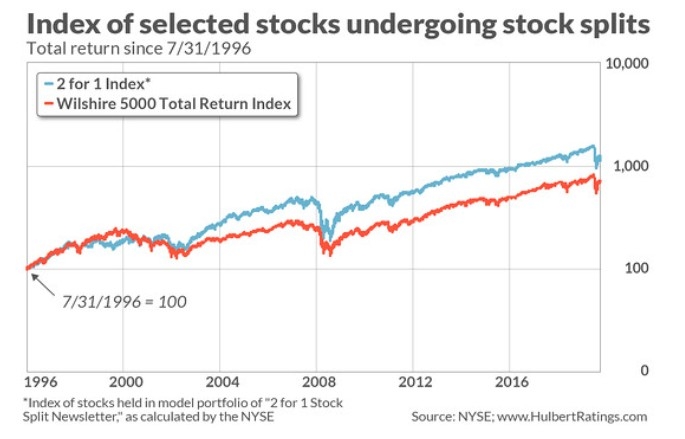
The early years of the stock market were marked by volatility and speculative bubbles. One of the most famous examples is the South Sea Bubble, which occurred in the 1720s. This bubble was fueled by the speculative buying of shares in the South Sea Company, which was granted a monopoly on trade with South America. The bubble burst, leading to widespread panic and economic turmoil.
Despite these early challenges, the stock market continued to grow and evolve. The Chicago Board of Trade was established in 1848, and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange was founded in 1853. These exchanges helped to provide liquidity and stability to the market.
The Great Depression of the 1930s had a profound impact on the stock market. In response, the government passed several laws to regulate the market and protect investors. The Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 were among the key legislative measures that helped to restore confidence in the market.
The Modern Stock Market
Today, the US stock market is one of the largest and most influential in the world. The NYSE and the NASDAQ Stock Market are two of the most prominent exchanges. The S&P 500 and the Dow Jones Industrial Average are among the most widely followed stock market indices.
The stock market has seen numerous innovations over the years. The advent of electronic trading platforms and the rise of online brokers have made it easier for individuals to invest in the stock market. Additionally, the development of new financial instruments, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and derivatives, has provided investors with more options to diversify their portfolios.
Case Study: The Tech Bubble of 2000
One of the most significant events in the history of the US stock market is the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s. This bubble was fueled by the rapid growth of technology companies, and many investors were optimistic about the future of the tech industry.
However, the bubble burst in 2000, leading to a significant decline in stock prices. This event highlighted the importance of conducting thorough research and understanding the risks associated with investing in the stock market.
Conclusion
The US stock market has a rich history that spans over two centuries. From its humble beginnings to its current status as a global financial powerhouse, the stock market has played a crucial role in the American economy. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the history of the stock market can provide valuable insights into its current state and future potential.