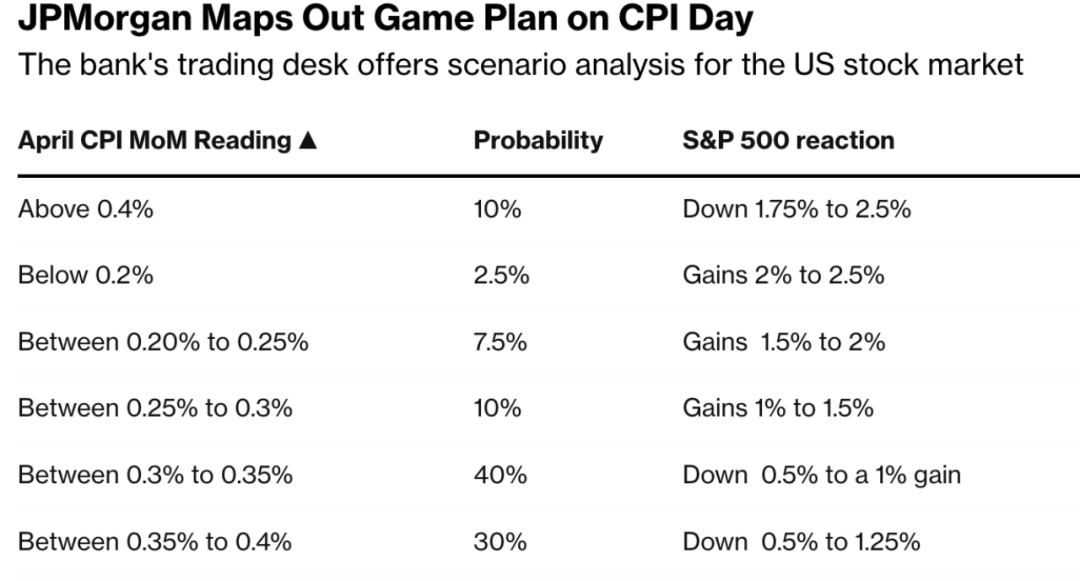
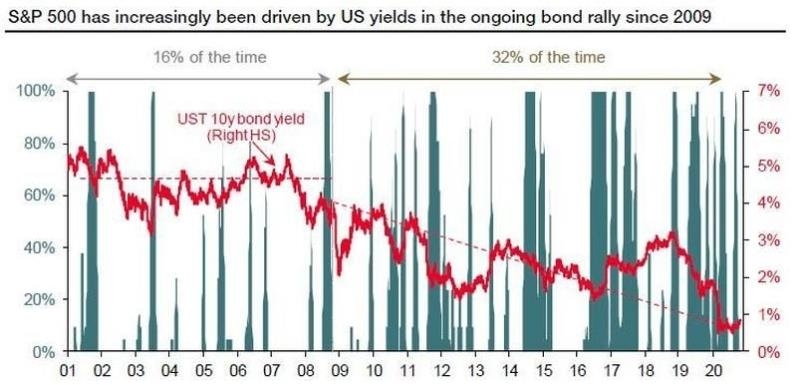
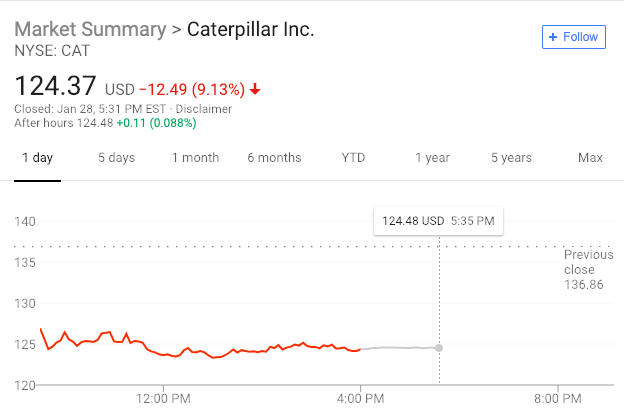
The stock market is often considered the heart of the financial world, and the United States stock market, in particular, has long been a beacon for investors and traders worldwide. However, the question of whether the US stock market is efficient has been a topic of debate for decades. In this article, we will delve into the concept of market efficiency, examine the factors that contribute to the efficiency of the US stock market, and analyze the evidence that supports or refutes the claim of efficiency.
Understanding Market Efficiency
Market efficiency refers to the degree to which stock prices reflect all available information. In an efficient market, stock prices are always "correct" and reflect all known information, making it impossible for investors to consistently achieve above-average returns by trading on that information.
The Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH)
The Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH) is a theory that suggests that stock prices always reflect all available information. According to the EMH, it is impossible to consistently outperform the market by using any information that is publicly available.
Factors Contributing to the Efficiency of the US Stock Market
Several factors contribute to the efficiency of the US stock market:
- High Level of Transparency: The US stock market is one of the most transparent markets in the world. Companies are required to disclose financial information, and this information is readily available to investors.
- High Level of Competition: The US stock market is highly competitive, with numerous investors and traders actively participating in the market. This competition ensures that stock prices quickly reflect all available information.
- Advanced Technology: The US stock market utilizes advanced technology to process and analyze information, which helps to ensure that stock prices are efficient.
- Regulatory Oversight: The US stock market is regulated by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which helps to maintain market integrity and ensure that all investors have access to the same information.
Evidence for Market Efficiency
Several pieces of evidence support the claim that the US stock market is efficient:
- Pricing Anomalies: Despite the EMH, there have been instances of pricing anomalies in the US stock market. However, these anomalies are often short-lived and quickly corrected by the market.
- Fama-French Three-Factor Model: The Fama-French Three-Factor Model suggests that the US stock market is efficient, as it explains most of the variation in stock returns.
- Market Index Performance: The performance of market indexes, such as the S&P 500, suggests that the US stock market is efficient, as these indexes closely track the overall market performance.
Evidence Against Market Efficiency
Despite the evidence supporting market efficiency, some argue that the US stock market is not entirely efficient:
- Pricing Anomalies: As mentioned earlier, there have been instances of pricing anomalies in the US stock market. These anomalies suggest that the market is not always able to fully incorporate all available information.
- Behavioral Finance: Behavioral finance suggests that investors are not always rational and can make mistakes, which can lead to inefficiencies in the market.
- Market Manipulation: Although rare, instances of market manipulation have occurred in the US stock market, which can lead to inefficiencies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the question of whether the US stock market is efficient is complex and multifaceted. While there is evidence to support the claim that the US stock market is efficient, there are also instances of inefficiencies. Ultimately, the answer to this question may depend on the specific context and the time frame being considered.