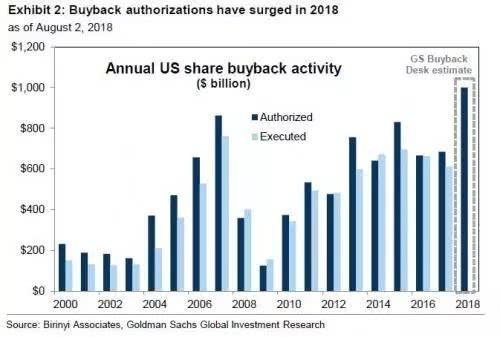
In the ever-evolving world of finance, understanding how to effectively allocate assets in the US stock market is crucial for investors seeking to maximize returns while managing risk. The US Stock Market Asset Allocation Model is a strategic approach that involves dividing an investment portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash, to achieve a balance between risk and return. This article delves into the key components of this model, its benefits, and real-world examples of its application.
What is the US Stock Market Asset Allocation Model?
The US Stock Market Asset Allocation Model is a method of dividing an investment portfolio among various asset classes based on an individual's risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. The primary objective is to create a diversified portfolio that offers the potential for growth while minimizing risk.

Key Components of the Model
Risk Tolerance: The level of risk an investor is willing to take plays a crucial role in determining the asset allocation. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to stocks, while those with a lower risk tolerance may prefer bonds and cash.
Investment Goals: Different investment goals require different asset allocations. For example, an investor aiming for long-term growth may allocate a higher percentage to stocks, while someone seeking capital preservation may prioritize bonds and cash.
Time Horizon: The time frame for achieving investment goals also influences asset allocation. Investors with a longer time horizon may be more comfortable with higher-risk assets, such as stocks, while those with a shorter time horizon may prefer lower-risk assets.
Asset Classes: The model typically includes three main asset classes: stocks, bonds, and cash. Each asset class has its own risk and return characteristics, and their allocation can be adjusted based on the investor's needs.
Benefits of the US Stock Market Asset Allocation Model
Diversification: By allocating assets across different classes, investors can reduce their exposure to market volatility and minimize the impact of any single asset's performance on their overall portfolio.
Risk Management: The model allows investors to tailor their portfolios to their risk tolerance, ensuring they are not taking on more risk than they can comfortably handle.
Potential for Growth: A well-diversified portfolio can provide the potential for long-term growth, as different asset classes may perform differently over time.
Real-World Examples
Consider an investor named John, who is 35 years old and aiming for long-term growth. Based on his risk tolerance and investment goals, he decides to allocate 60% of his portfolio to stocks, 30% to bonds, and 10% to cash. This allocation allows him to benefit from the potential growth of the stock market while also providing some stability through bonds and cash.
Another investor, Sarah, who is 55 years old and nearing retirement, may have a different asset allocation. With a lower risk tolerance and a focus on capital preservation, she may allocate 40% to bonds, 30% to stocks, and 30% to cash.
Conclusion
The US Stock Market Asset Allocation Model is a valuable tool for investors seeking to create a well-diversified and balanced portfolio. By understanding the key components and benefits of this model, investors can make informed decisions that align with their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon.