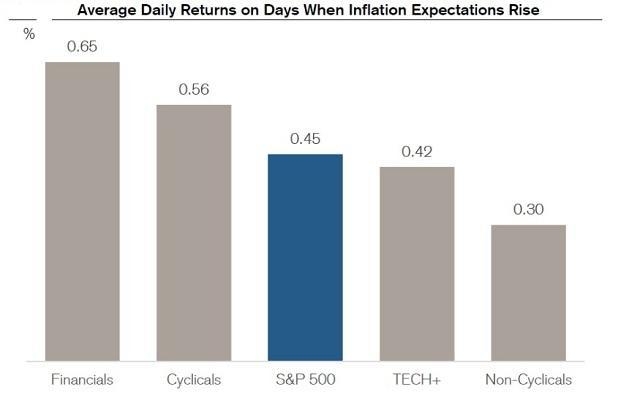
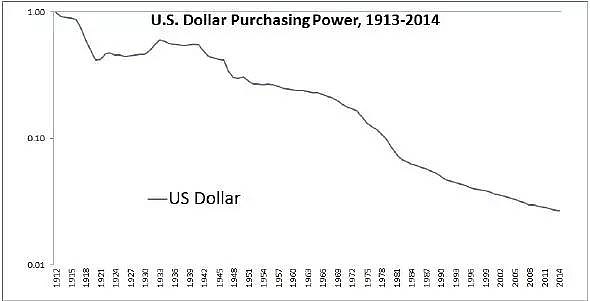
In the world of finance, the United States stock and bond markets are two of the most significant and influential platforms. Whether you are an experienced investor or just starting out, understanding the nuances of these markets can significantly impact your financial decisions. This article delves into the basics of US stocks and bonds, highlighting their key characteristics, risks, and potential returns.
US Stocks: The Heart of the Market
US stocks represent ownership in a company. When you purchase shares of a company, you become a partial owner, entitled to a portion of the company's profits. The stock market is a dynamic place, with prices fluctuating based on various factors, including company performance, economic conditions, and investor sentiment.
Key Characteristics of US Stocks
- Ownership: When you buy stocks, you own a piece of the company.
- Dividends: Some companies distribute dividends to shareholders, which can provide a steady income stream.
- Capital Gains: If the stock price rises, you can sell your shares at a profit.
- Risks: Stock prices can be volatile, and there is always the risk of losing your investment.
Types of US Stocks
- Common Stocks: These represent ownership in the company and come with voting rights.
- Preferred Stocks: These offer fixed dividends and may have priority over common stocks in case of bankruptcy.
US Bonds: The Steady Hand in the Market
On the other hand, US bonds are debt instruments issued by the government or corporations to raise capital. When you buy a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity.
Key Characteristics of US Bonds
- Fixed Income: Bonds provide a predictable stream of income through regular interest payments.
- Maturity: Bonds have a fixed maturity date, after which the principal amount is returned.
- Credit Risk: The risk of default is higher for corporate bonds compared to government bonds.
Types of US Bonds
- Treasury Bonds: Issued by the US government, these are considered to be the safest investment.
- Corporate Bonds: Issued by corporations, these carry a higher risk but offer higher yields.
- Municipal Bonds: Issued by state and local governments, these are tax-exempt and considered to be a good investment for income.
Case Study: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
To illustrate the difference between stocks and bonds, let's take a look at Apple Inc. (AAPL). As one of the largest companies in the world, Apple offers both stocks and bonds.
- Stocks: Investors who bought Apple stocks in 2003 have seen their investment grow significantly. However, the stock price can be volatile, and there is always the risk of losing your investment.
- Bonds: Apple also issued bonds, which provided investors with a steady stream of income. These bonds were considered to be relatively safe, as Apple is a well-established company with a strong financial position.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of US stocks and bonds is crucial for making informed investment decisions. While stocks offer the potential for high returns, they come with higher risks. Bonds, on the other hand, provide a steady income stream but with lower returns. As an investor, it is essential to assess your risk tolerance and investment goals before deciding which asset class to invest in.