In the dynamic world of business, understanding the intricacies of a stock company is crucial for anyone looking to invest, start, or grow a business in the United States. A stock company, often referred to as a corporation, is a legal entity that offers shares to the public, allowing individuals and institutions to invest in its operations. This guide will delve into the essential aspects of stock companies in the US, from their formation to their impact on the economy.
Understanding Stock Companies
A stock company is a type of business organization that is owned by shareholders. These shareholders purchase shares of the company, which represent a portion of the company's ownership. The most common types of stock companies in the US are C Corporations and S Corporations.
C Corporations: These are the most common type of stock company. They offer limited liability protection to their shareholders, meaning that shareholders are not personally liable for the company's debts. However, C Corporations are subject to double taxation, as the company pays taxes on its profits, and shareholders pay taxes on dividends received.
S Corporations: These are pass-through entities, meaning that the company's profits and losses are passed through to the shareholders, who then pay taxes on their individual tax returns. S Corporations offer limited liability protection, but they have stricter requirements for shareholder人数 and ownership structure.
The Process of Forming a Stock Company
Forming a stock company in the US involves several steps. The first step is to choose a state of incorporation. While many businesses choose to incorporate in Delaware due to its favorable corporate laws, other states like Nevada and Wyoming also offer attractive options.
Once a state is chosen, the next step is to file articles of incorporation with the state's secretary of state. This document includes the company's name, purpose, and the names and addresses of its initial directors and shareholders.
After filing the articles of incorporation, the company must obtain any necessary licenses and permits, open a business bank account, and draft its bylaws and operating agreement. The bylaws outline the company's internal governance, while the operating agreement governs the relationship between the shareholders.
The Role of Stock Companies in the Economy
Stock companies play a vital role in the US economy. They provide a platform for businesses to raise capital, which can be used for expansion, research and development, and other business activities. This, in turn, stimulates economic growth and job creation.
Moreover, stock companies offer investors a way to diversify their portfolios and potentially earn returns through dividends and capital gains. The stock market, which is a reflection of the performance of stock companies, is a key indicator of the overall health of the economy.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of stock companies, let's consider two well-known examples: Apple Inc. and Amazon.com Inc.
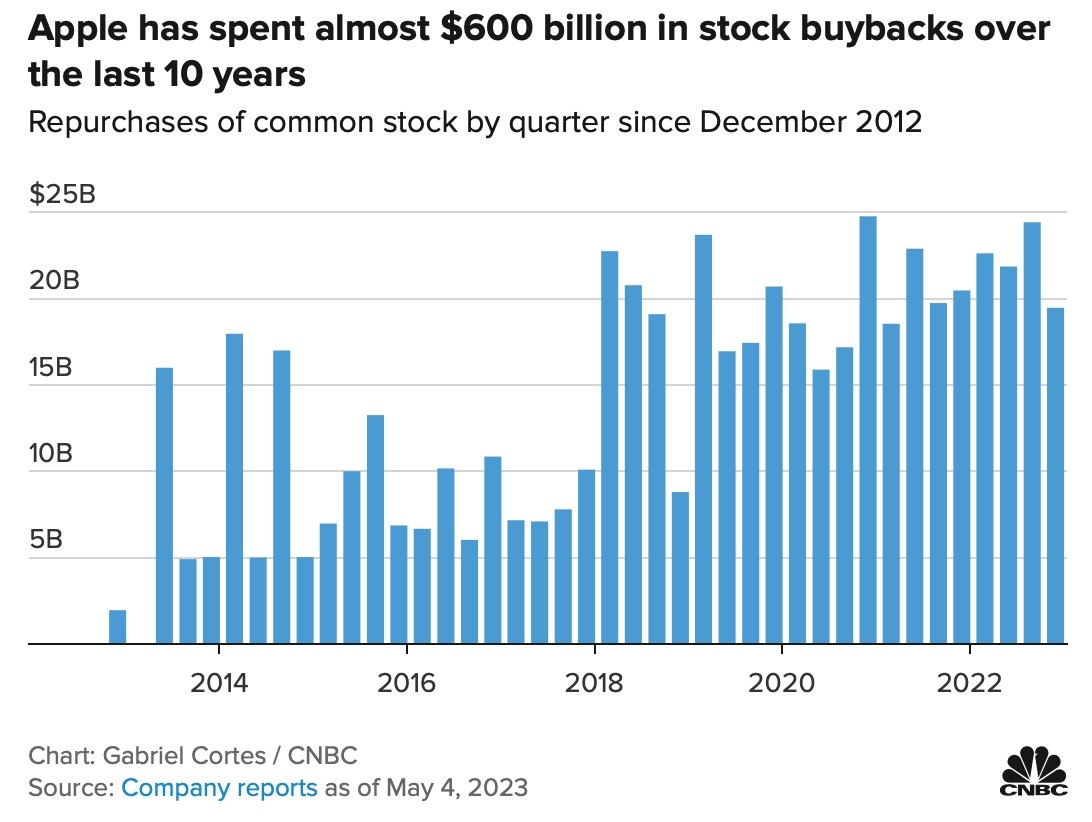
Apple Inc.: Founded in 1976, Apple is a prime example of a successful stock company. The company has revolutionized the technology industry with its innovative products, such as the iPhone, iPad, and Mac computer. Apple's stock has seen significant growth over the years, making it one of the most valuable companies in the world.
Amazon.com Inc.: Founded in 1994, Amazon has transformed the retail industry by offering a vast selection of products at competitive prices. The company has expanded into various sectors, including cloud computing, streaming, and artificial intelligence. Amazon's stock has also experienced substantial growth, making it a leading player in the stock market.
Conclusion
Understanding stock companies in the US is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complex world of business and investment. By familiarizing themselves with the formation, operation, and impact of stock companies, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and contribute to the growth of the US economy.