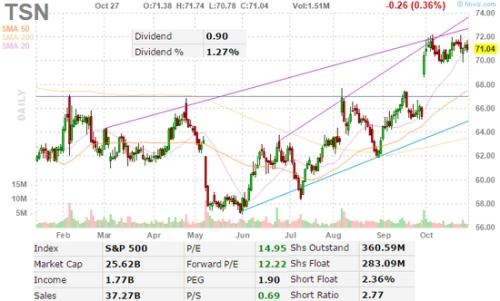
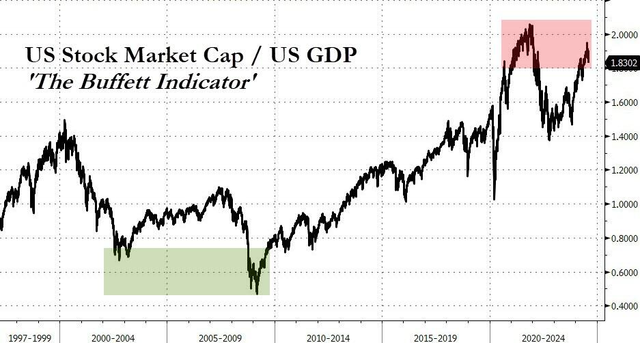
In the intricate world of finance, the relationship between interest rates and the US stock market is a topic that often garners significant attention. This article delves into how changes in interest rates can impact the US stock market, offering insights for investors looking to navigate this complex relationship.
Understanding the Basics
Interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve, are a critical economic indicator. They influence borrowing costs, consumer spending, and business investment. The US stock market, on the other hand, is a reflection of the overall economic health and sentiment of investors.
When interest rates are low, it typically indicates a healthy economy. This scenario is beneficial for stocks, as lower borrowing costs encourage companies to invest and expand. Conversely, when interest rates are high, it suggests a potential economic slowdown. This situation can negatively impact stocks, as higher borrowing costs can lead to reduced corporate earnings.
The Impact of Low Interest Rates on US Stocks
When interest rates are low, it generally results in the following outcomes for the US stock market:
- Increased Stock Prices: Lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing, making it easier for companies to finance their operations and expand. This often leads to higher earnings and, subsequently, increased stock prices.
- Attractive Dividend Yields: Companies with high dividend yields become more appealing to investors, as they offer a competitive return relative to the low interest rate environment.
- M&A Activity: Low interest rates can stimulate merger and acquisition activity, as companies can borrow at cheaper rates to finance these transactions.
The Impact of High Interest Rates on US Stocks
Conversely, when interest rates are high, the US stock market may experience the following effects:
- Lower Stock Prices: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for companies, which can lead to reduced earnings and, consequently, lower stock prices.
- Reduced Dividend Yields: As borrowing costs rise, companies may be less inclined to distribute dividends, resulting in lower yields for investors.
- Increased Volatility: The stock market tends to become more volatile in high-interest rate environments, as investors react to changing economic conditions and corporate earnings.
Case Study: The 2018 Stock Market Correction
A notable example of the impact of interest rates on the US stock market is the 2018 correction. In late 2018, the Federal Reserve raised interest rates, which led to increased borrowing costs for companies. This, coupled with concerns about global economic growth, caused the stock market to experience significant volatility and a correction.
Conclusion
The relationship between interest rates and the US stock market is a complex one. While low interest rates generally benefit stocks, high interest rates can have a negative impact. Investors need to be aware of these dynamics and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. By understanding the impact of interest rates on the stock market, investors can make more informed decisions and navigate the ever-changing financial landscape.