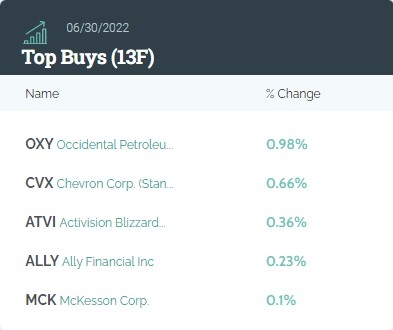
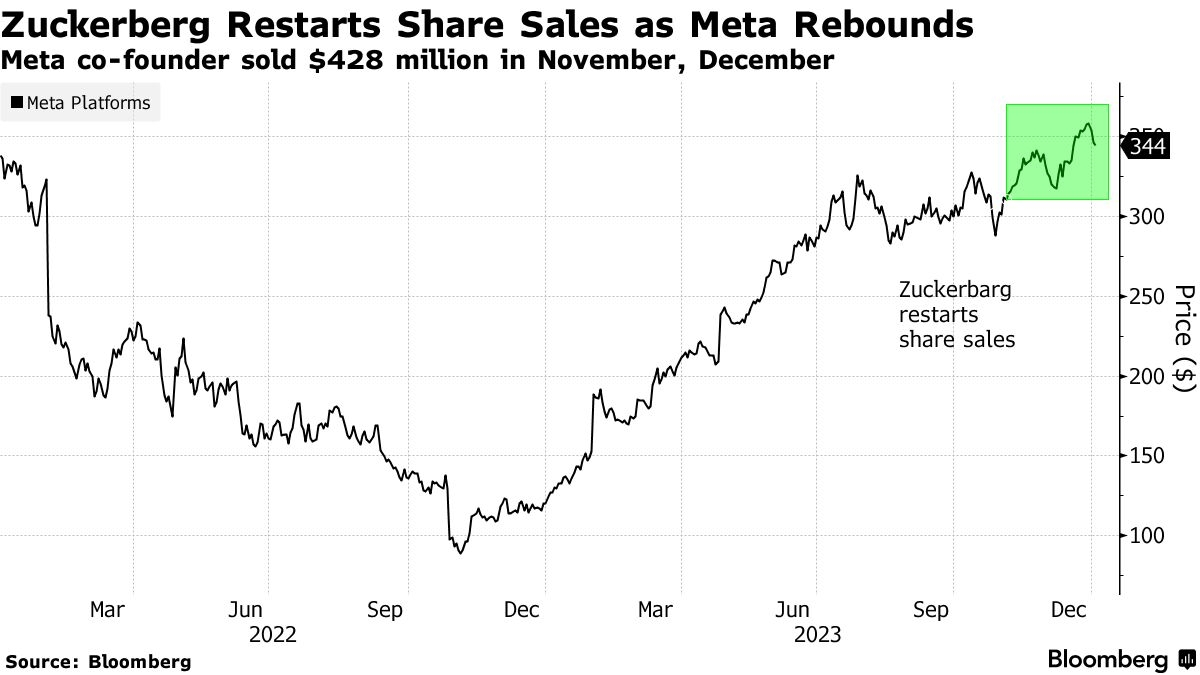
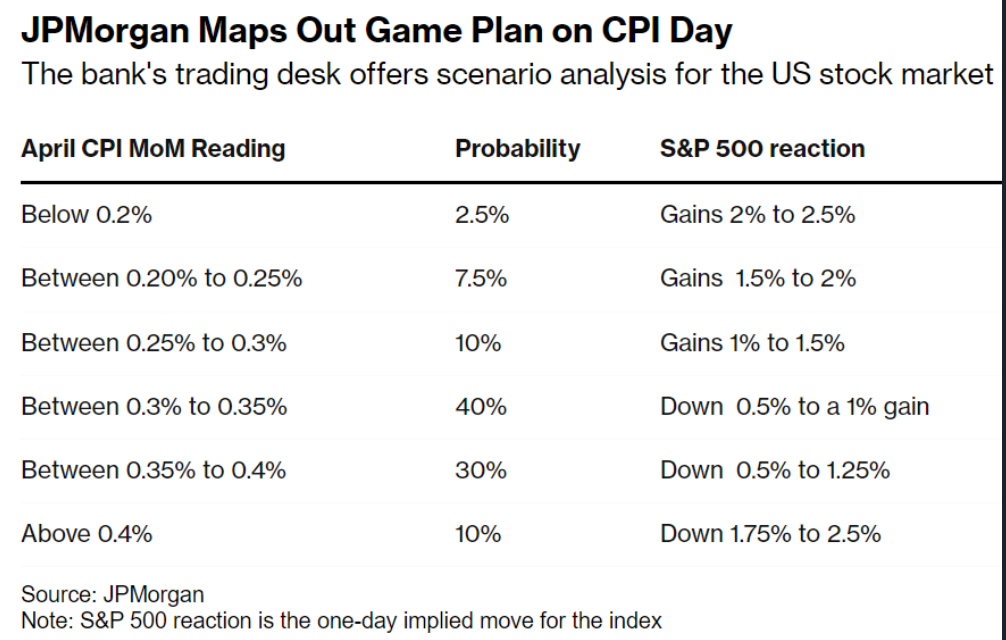
Introduction:
The US government shutdown, a recurring event in recent years, has become a major concern for investors and economists alike. With the potential to disrupt economic activities and create uncertainty, the impact of these shutdowns on the stock market cannot be overlooked. This article delves into the effects of government shutdowns on the stock market, analyzing both short-term and long-term consequences.
Short-term Effects:
During a government shutdown, the immediate impact on the stock market is often negative. Investors tend to become wary of uncertainty, leading to a sell-off of stocks. This is particularly true for sectors that are heavily dependent on government spending, such as defense, transportation, and healthcare.
One of the primary reasons for this negative impact is the halt in government operations. With non-essential government employees furloughed or working without pay, there is a decrease in government spending, which can have a ripple effect on the economy. As a result, companies in these sectors may experience reduced revenue and profits, leading to a decline in their stock prices.
Another factor contributing to the short-term negative impact is the uncertainty surrounding the duration of the shutdown. Investors often react to uncertainty by selling off stocks, hoping to minimize potential losses. This selling pressure can further exacerbate the downward trend in the stock market.
Long-term Effects:
While government shutdowns can have immediate negative effects on the stock market, their long-term impact can vary. In some cases, shutdowns have been followed by a period of economic recovery and a subsequent rise in stock prices.
One possible explanation for this is the government's eventual resolution of the shutdown. Once the government reopens, it can resume its spending and support for various sectors of the economy. This can lead to increased economic activity and, subsequently, higher stock prices.

Additionally, the long-term impact of a shutdown can depend on the underlying causes of the shutdown. For example, a shutdown caused by a budget dispute may have a more significant long-term impact than a shutdown caused by a temporary funding shortfall.
Case Study: The 2018 Shutdown
In January 2018, the US government experienced a 35-day shutdown due to a budget dispute. During this period, the stock market experienced significant volatility. Initially, the shutdown led to a sell-off of stocks, particularly in sectors heavily dependent on government spending. However, once the government reopened, the stock market began to recover, with many indices reaching new highs by the end of the year.
This case study illustrates the potential for long-term recovery following a government shutdown. While the immediate impact is often negative, the eventual resolution of the shutdown can lead to economic recovery and a subsequent rise in stock prices.
Conclusion:
The impact of US government shutdowns on the stock market is a complex issue with both short-term and long-term consequences. While shutdowns can lead to immediate negative effects, the long-term impact can vary depending on the underlying causes and the government's resolution of the shutdown. As investors and economists continue to monitor these events, it is crucial to understand the potential risks and opportunities they present.