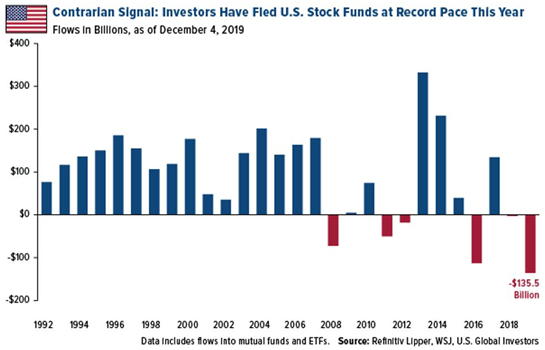
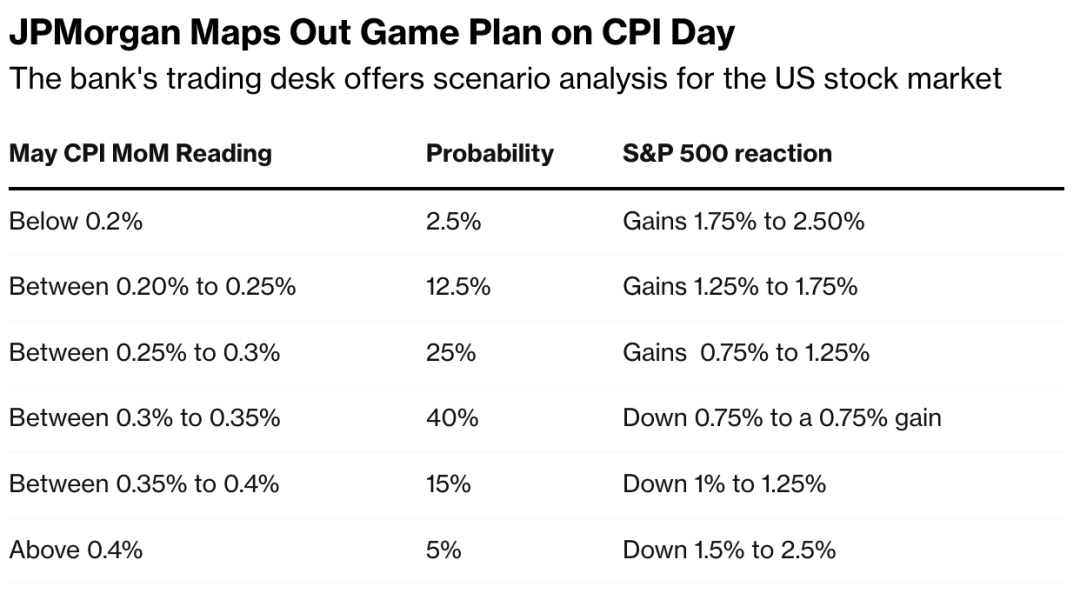
The US stock market is a vast and dynamic landscape, with numerous players contributing to its day-to-day operations. Among these players, big market makers stand out as pivotal figures. These entities play a crucial role in maintaining the liquidity and stability of the market. In this article, we delve into the world of big market makers, exploring their significance, operations, and impact on the US stock market.
Understanding Big Market Makers
Big market makers, also known as specialists, are financial institutions that provide liquidity to the market by continuously offering to buy and sell stocks. They act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, ensuring that there is a constant flow of shares available for trading. These institutions typically have a significant amount of capital at their disposal, allowing them to influence stock prices and market dynamics.
The Role of Big Market Makers
The primary role of big market makers is to facilitate trading and maintain fair and efficient markets. Here are some key functions they perform:
- Providing Liquidity: By offering to buy and sell stocks, big market makers ensure that there is a constant supply of shares available for trading. This liquidity enables investors to enter and exit positions with ease.
- Stabilizing Prices: Big market makers closely monitor stock prices and adjust their bids and offers accordingly. This helps in stabilizing prices and preventing excessive volatility.
- Facilitating Arbitrage Opportunities: Big market makers identify price discrepancies between different exchanges and execute trades to profit from these opportunities. This process helps in ensuring that prices remain aligned across different platforms.
Operations of Big Market Makers
Big market makers operate through a sophisticated system of algorithms and human traders. Here's an overview of their operations:
- Monitoring Market Data: Big market makers continuously monitor market data, including stock prices, trading volumes, and news feeds, to stay informed about market conditions.
- Setting Bids and Offers: Based on their analysis of market conditions, big market makers set their bids and offers for stocks. They aim to buy stocks at a lower price and sell them at a higher price, thereby generating profits.
- Executing Trades: When a buyer or seller enters a trade, big market makers execute the trade on their behalf, ensuring that the transaction is completed smoothly.
- Adjusting Positions: Big market makers continuously adjust their positions based on market conditions and their own strategies.
Impact on the US Stock Market
Big market makers have a significant impact on the US stock market. Here are some key impacts:
- Enhanced Liquidity: The presence of big market makers ensures that there is a constant flow of shares available for trading, making the market more accessible to investors.
- Stabilized Prices: The efforts of big market makers to stabilize prices help in reducing volatility and providing a more predictable trading environment.
- Increased Efficiency: By facilitating trading and arbitrage opportunities, big market makers contribute to the overall efficiency of the market.
Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of big market makers, let's consider a few case studies:
- Facebook IPO: During Facebook's initial public offering (IPO) in 2012, big market makers played a crucial role in ensuring the smooth execution of trades. Their efforts helped in stabilizing the stock price and facilitating the transition from private to public markets.
- Tesla's Stock Surge: In 2020, Tesla's stock experienced a significant surge in value. Big market makers played a role in supporting the stock price and providing liquidity during this period.

Conclusion
Big market makers are essential players in the US stock market, providing liquidity, stabilizing prices, and enhancing market efficiency. Their operations and impact are significant, and their role is likely to continue evolving in the future. As investors and traders, understanding the role of big market makers can help us navigate the complexities of the stock market and make more informed decisions.