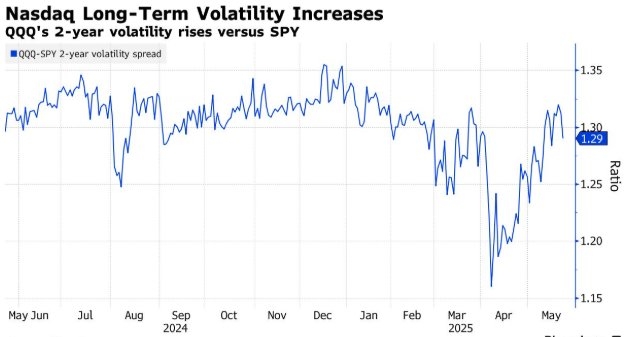
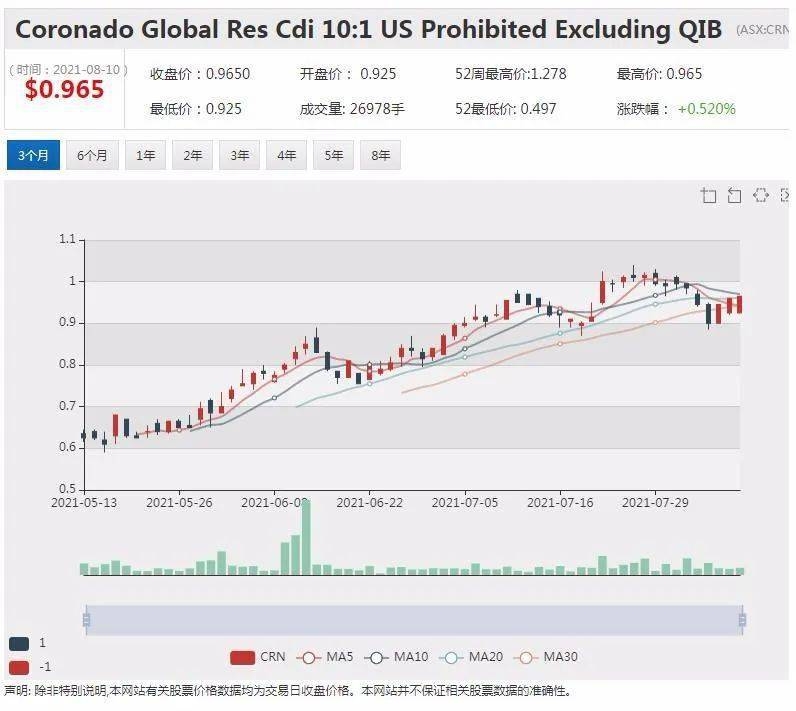
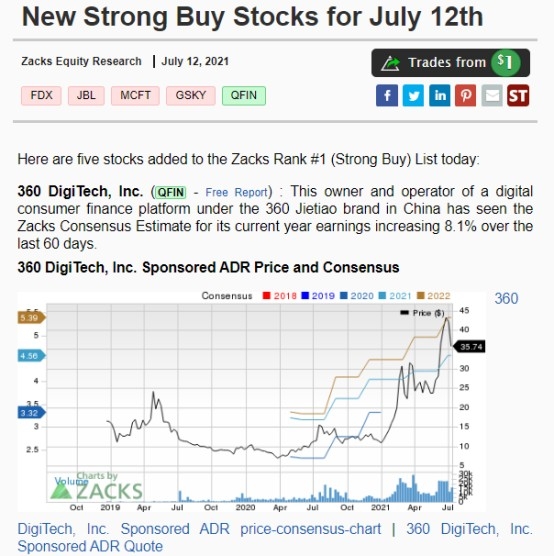
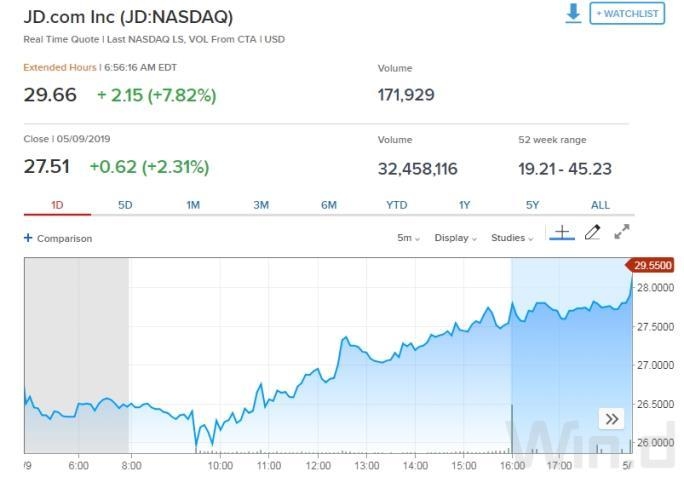
Introduction:
In the world of financial markets, futures contracts play a crucial role in hedging risks and speculating on price movements. The NQ100 futures, also known as the NASDAQ 100 futures, are among the most popular and liquid futures contracts available. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to trading and investing in NQ100 futures, covering key aspects such as contract specifications, trading strategies, and potential risks.
Understanding the NQ100 Futures Contract
The NQ100 futures contract is based on the NASDAQ-100 Index, which tracks the performance of the 100 largest non-financial companies listed on the NASDAQ exchange. This index represents a diverse range of sectors, including technology, healthcare, and consumer discretionary.
Key Features of the NQ100 Futures Contract:
- Contract Size: The NQ100 futures contract has a multiplier of 100, meaning that a single contract represents $100 times the index value.
- Trading Hours: The NQ100 futures contract is traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and follows the regular trading hours of the NASDAQ exchange.
- Expiry: The NQ100 futures contract has a monthly expiry date, with contracts expiring on the third Friday of each month.
Trading Strategies for NQ100 Futures
- Speculation: Traders can speculate on the direction of the NASDAQ-100 Index by taking long or short positions in NQ100 futures contracts.
- Hedging: Investors holding NASDAQ-100 stocks can use NQ100 futures to hedge their portfolio against market risks.
- Arbitrage: Arbitrageurs can take advantage of price discrepancies between the NQ100 futures and the underlying index by simultaneously buying and selling the two instruments.
Risk Management in NQ100 Futures Trading
It is essential to manage risks effectively when trading NQ100 futures. Here are some key risk management strategies:
- Stop-Loss Orders: Place stop-loss orders to limit potential losses in case the market moves against your position.
- Position Sizing: Avoid over-leveraging by maintaining a well-diversified portfolio and managing position sizes appropriately.
- Market Analysis: Conduct thorough market analysis and stay updated with economic news and events that can impact the NASDAQ-100 Index.
Case Study: NQ100 Futures Trading
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario where a trader believes that the NASDAQ-100 Index will rise in the near future. The trader decides to take a long position in NQ100 futures contracts by buying 10 contracts at a price of $12,500 per contract.
Assumptions:
- The trader's margin requirement is $5,000 per contract.
- The index value at the time of buying is 12,000.
Potential Profit Calculation:
If the index value rises to 12,500, the trader will make a profit of
Conclusion
The NQ100 futures contract offers traders and investors a valuable tool for speculating on the NASDAQ-100 Index and hedging risks. By understanding the contract specifications, trading strategies, and risk management techniques, investors can make informed decisions and potentially achieve profitable outcomes in the NQ100 futures market.