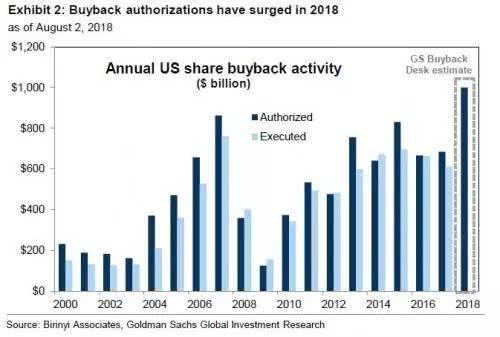
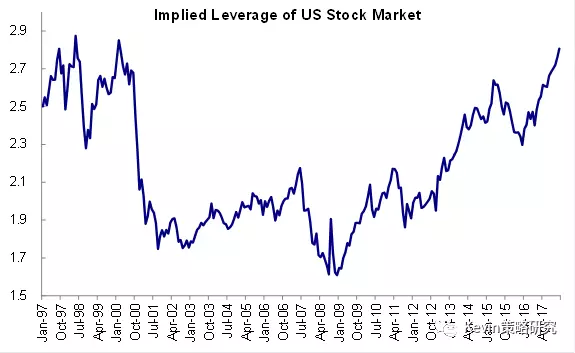
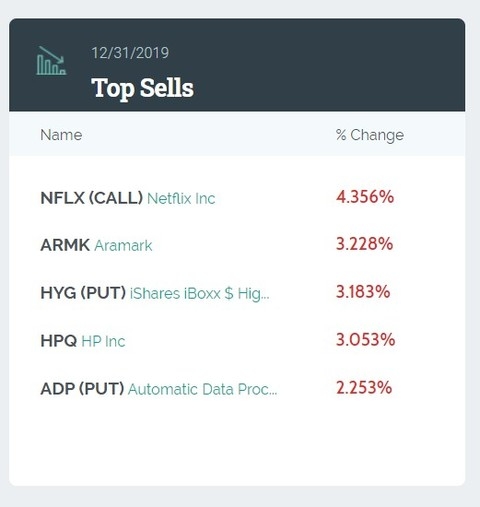
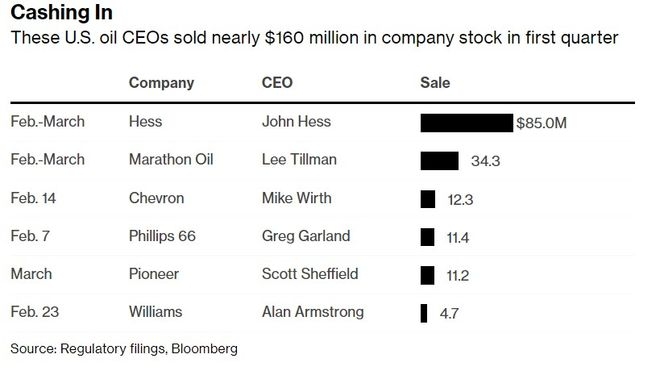
Understanding the Basics of the US Stock Market
The US stock market is one of the most dynamic and influential financial markets in the world. It is a place where companies raise capital, investors make money, and economic trends are set. If you're new to the world of investing, it's important to understand how the US stock market works. This article will break down the basics, so you can start making informed decisions.
What is the Stock Market?
The stock market is a marketplace where shares of publicly-traded companies are bought and sold. When you buy a stock, you're essentially purchasing a small piece of that company. The value of your investment can increase or decrease based on the company's performance and the overall market conditions.
How Does the Stock Market Work?
The US stock market operates through a network of stock exchanges, the most well-known being the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. Here's a simplified breakdown of how it works:
Listing a Company: A company decides to go public by filing an Initial Public Offering (IPO). This process involves registering with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and issuing shares to the public.
Trading: Once a company is listed, its shares can be bought and sold on the stock exchanges. Investors can place buy or sell orders through brokerage firms.
Order Execution: When you place an order to buy or sell a stock, your brokerage firm will execute the trade. This can happen on the same day or over a few days, depending on the market conditions.
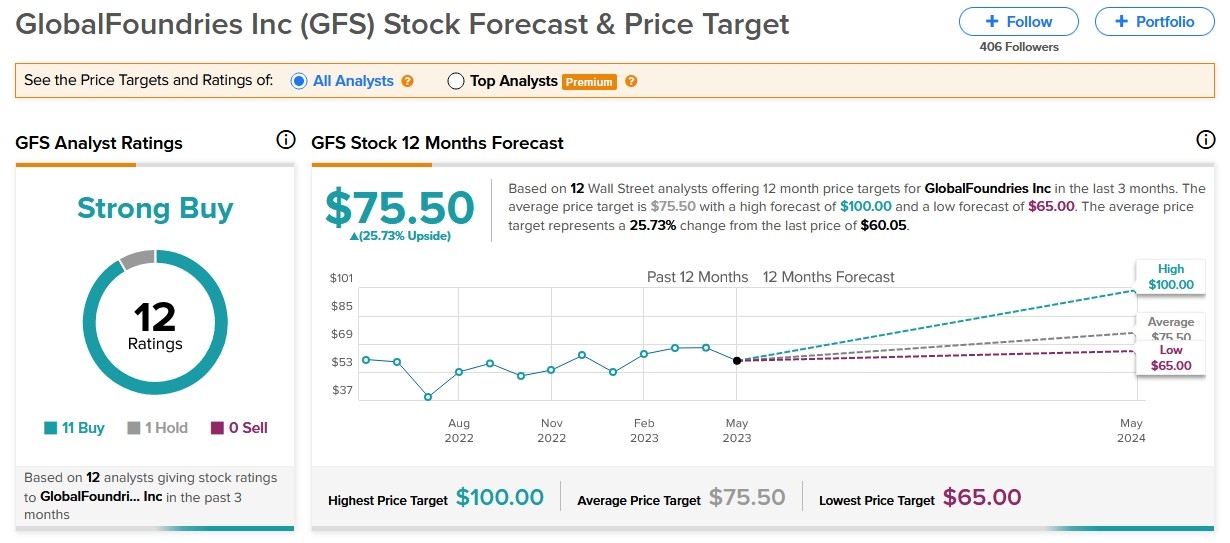
Market Price: The price at which a stock is bought or sold is determined by the supply and demand for that stock. If more people want to buy a stock than sell it, the price will increase. Conversely, if more people want to sell a stock than buy it, the price will decrease.
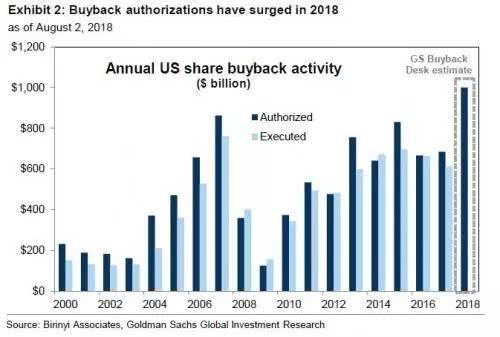
Dividends: Some companies distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. Dividends can be a source of income for investors and can also affect the stock's price.
Market Indices: The performance of the stock market is often measured by market indices, such as the S&P 500, the Dow Jones Industrial Average, and the NASDAQ Composite. These indices track the performance of a basket of stocks and are used to gauge the overall market trends.
Key Players in the Stock Market
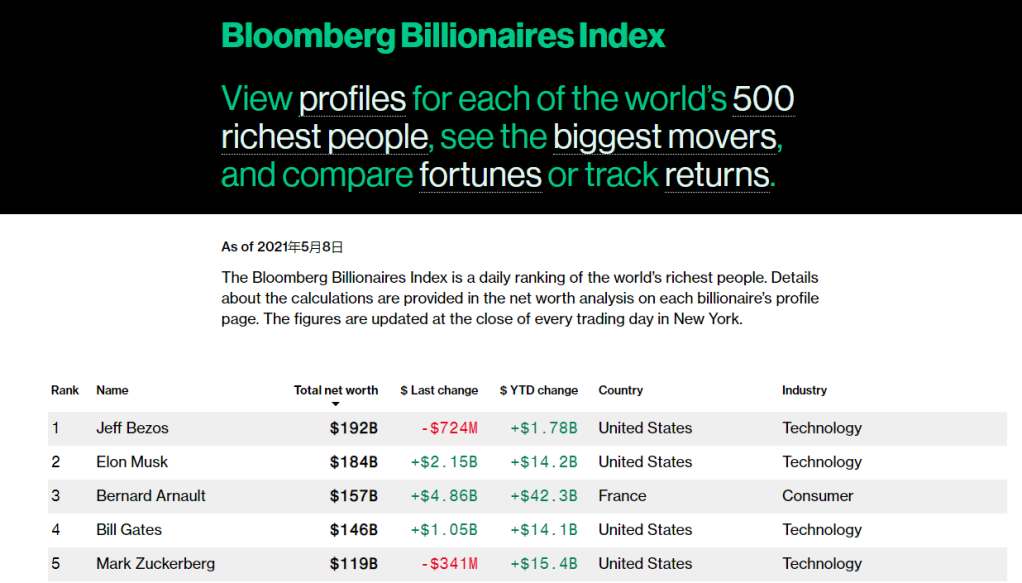
- Investors: Individuals and institutions that buy and sell stocks.
- Brokers: Financial intermediaries that facilitate the buying and selling of stocks on behalf of investors.
- Market Makers: Financial firms that provide liquidity in the market by buying and selling stocks.
- Regulators: Government agencies, such as the SEC, that oversee the stock market to ensure fair and transparent trading.
Case Study: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Apple Inc. is a prime example of a company that has thrived in the US stock market. In 1980, Apple went public at
Conclusion
Understanding how the US stock market works is crucial for anyone looking to invest. By familiarizing yourself with the basics, you can make informed decisions and potentially grow your wealth. Remember, investing in the stock market carries risks, so it's important to do your research and consider your financial goals.